TL;DR
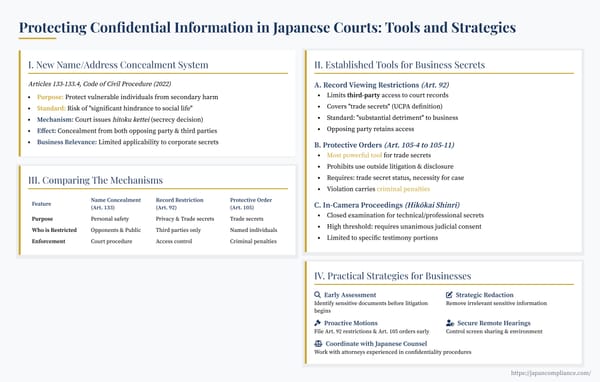
* Japan lacks US-style broad discovery, but IP litigants have targeted tools: pre-suit evidence preservation, document production orders with in-camera review, court inspections, and the new expert-led sashou system.
* Success hinges on early assessment, specific requests, and strategic use of these court-controlled mechanisms while safeguarding trade secrets with protective